What is incident management? ITIL practices explained
Efficient IT systems are the foundation of any modern business, where unexpected disruptions can halt operations, hinder productivity, and lead to significant financial losses. This is where Incident Management, a core component of the ITIL framework, plays a vital role in maintaining stability and minimizing impact.
Topics Covered
Introduction
Incident Management is a fundamental practice within the ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework, designed to address unplanned interruptions or disruptions to IT services. It focuses on swiftly restoring normal service operations, minimizing the impact on productivity, and ensuring seamless organizational performance. Whether dealing with minor slowdowns or major outages, the goal of Incident Management is consistent and clear—resolve issues quickly and effectively to maintain uninterrupted service delivery.
Within the ITIL framework, incidents are defined as any event that interrupts the normal flow of IT services or reduces their quality. This process is integral to the broader IT Service Management (ITSM) approach, which emphasizes structured service delivery and operational excellence. By streamlining the detection, analysis, and resolution of these incidents, Incident Management supports ITIL’s core principle of enabling businesses to function efficiently in a technology-dependent environment.
Serving as a link between IT services and business continuity, Incident Management ensures that IT systems remain reliable and responsive even in the face of unexpected challenges, enabling organizations to be better equipped to handle disruptions, safeguard service reliability, and maintain the trust of their users.
Terminology
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
Escalation |
When an incident or service request exceeds current support capabilities, escalation occurs. ITIL defines two types: functional and hierarchical. Both work together to resolve issues effectively. |
Incident Management |
The goal of incident management is to swiftly reduce disruptions by restoring normal service operations. This minimizes the negative effects of incidents on business functions. |
Incident |
An incident refers to an unplanned interruption or a reduction in the quality of a service. It’s often the starting point for identifying and resolving service issues. |
Target Response Time |
This is the maximum time a support team commits to respond to an incident or service request after it’s reported by a user. A timely response is key to maintaining service satisfaction. |
Target Resolution Time |
This term defines the maximum time allocated for resolving an incident or service request. It ensures clear expectations for users while holding support teams accountable for quick resolutions. |
Ticket |
A ticket is a datacard within a service management tool that represents incidents, service orders, or requests for information. It functions as a record that tracks progress and provides essential details. |
Priority |
Priority reflects the urgency and importance of an incident or service request. It’s determined by its business impact and how quickly resolution is needed. |
Service Level Agreement (SLA) |
An SLA is a formal agreement defining expected levels of service performance and quality. Represented as a service level record, it helps ensure that service expectations are clear and measurable. |
Knowledge Base Article |
These articles provide users with step-by-step guidance, screenshots, and other resources to resolve common issues. By empowering users to troubleshoot independently, knowledge base articles reduce the load on support teams. |
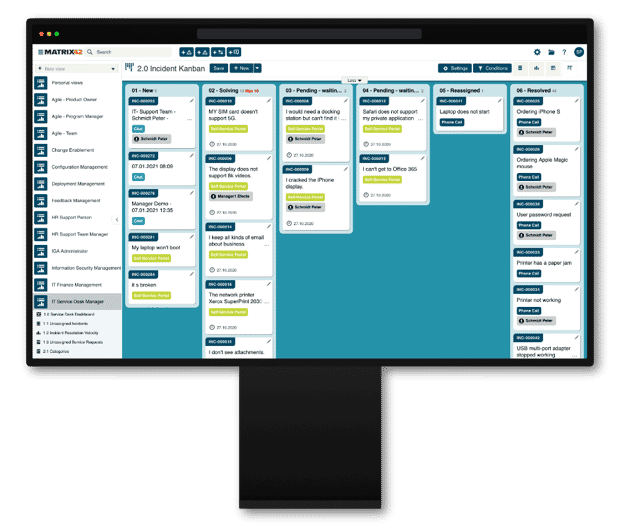
The Incident Management Process
Incident identification
Incident Logging
Record all relevant details, such as time, description, and affected systems, in a centralized system.
Categorization and Prioritization
Classify incidents based on type and urgency, assigning priority levels based on impact and urgency to ensure critical issues are addressed first.
Initial Diagnosis
Perform a preliminary analysis to identify potential solutions or escalate the issue if needed.
Escalation
Route complex or unresolved incidents to higher-level support teams for further investigation through escalation. According to ITIL, escalation can be divided into two types: functional escalation, and hierarchical escalation.
Resolution and Recovery
Implement a solution to restore normal services and verify the fix with the user.
Incident Closure
Confirm the resolution with the user and document the resolution details for future reference.
Review and Reporting
Analyze patterns, identify recurring issues, and refine processes to enhance future incident management practices.
The ITIL incident management process ensures efficient handling of IT service disruptions to minimize impact on business operations.
Best practices for Incident Management
Implementing effective incident management requires adherence to best practices. Below are some critical ones aligned with ITIL 4 recommendations:

- Incident Categorization & Prioritization:
Clearly categorize incidents based on their type and severity. This ensures the most critical issues are identified and addressed first. - Defined Escalation Procedures:
Establish clear rules for escalating incidents to different levels of support (e.g., from 1st Level to 2nd Level). - Use of Automation Tools
Leverage incident management tools to automate detection, notification, and tracking for improved efficiency. - Post-Incident Reviews:
Conduct detailed post-mortems after major incidents to identify root causes, learn lessons, and improve future processes. - Proactive Communication:
Keep users informed about incident status and resolution through regular updates.
By following these best practices, organizations can enhance response speed, ensure accountability, and reduce the overall cost of incident resolution.
The Role of Incident Management in ITIL
Incident Management is a cornerstone of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), serving as a critical component within the broader IT service management (ITSM) framework. ITIL promotes a systematic approach to managing incidents, ensuring alignment with key business objectives. Here’s how Incident Management integrates with ITIL principles:
- Core to IT Service Management (ITSM):
Incident Management prioritizes end-user satisfaction and ensures uninterrupted service delivery, making it a fundamental element of ITSM.
- Collaboration with Problem Management:
While Incident Management focuses on resolving immediate issues, Problem Management dives deeper to find and address root causes, preventing future incidents.
- Handling Major Incidents:
ITIL provides structured methodologies to manage high-impact incidents affecting critical business services. These frameworks enable swift resolutions to minimize downtime and business disruption.
- Commitment to Continuous Improvement:
ITIL emphasizes the need to continually refine Incident Management processes, adapting to evolving technology and organizational demands.
- Integration with Other ITIL Processes:
Incident Management works closely with several ITIL practices to ensure a seamless response to IT disruptions:
- Event Management: Monitors systems to detect conditions requiring action, often triggering incident records.
- Problem Management: Supplies insights such as workarounds and known errors to aid incident resolution while leveraging incident data for root cause analysis.
- Change Management: Activated when a change is necessary to resolve an incident, ensuring the modification is controlled and effective.
- Configuration Management: Provides detailed data on configuration items (CIs), helping teams identify incidents and link them to affected components.
Why it Matters
Efficient Incident Management under the ITIL framework ensures that disruptions are resolved quickly and effectively. By fostering service continuity and maintaining alignment with business goals, it enables IT teams to deliver robust support that keeps organizations running smoothly.

Matrix42 Recognized as a Strong Performer in the 2025 Gartner® "Voice of the Customer” for IT Service Management Platforms published in July 2025.
August 05, 2025